
In contrast, companies with low operating leverage have cost structures comprised of comparatively more variable costs that are directly tied to production volume. Running a business incurs a lot of costs, and not all these costs are variable. In other words, there are some costs that have to be paid even if the company has no sales. These types of expenses are called fixed costs, and this is where Operating Leverage comes from. As it pertains to small businesses, it refers to the degree of increase in costs relative to the degree of increase in sales.
- Once they have covered their fixed costs, they have the ability to increase their operating income considerably with higher sales output.
- If a company has high operating leverage, then it means that a large proportion of its overall cost structure is due to fixed costs.
- The degree of operating leverage allows the investors to understand many factors regarding to the company.
- It wouldn’t be wrong to say that high DOL is the companion of good times.
- After the collapse of dotcom technology market demand in 2000, Inktomi suffered the dark side of operating leverage.
Operating Leverage Formula
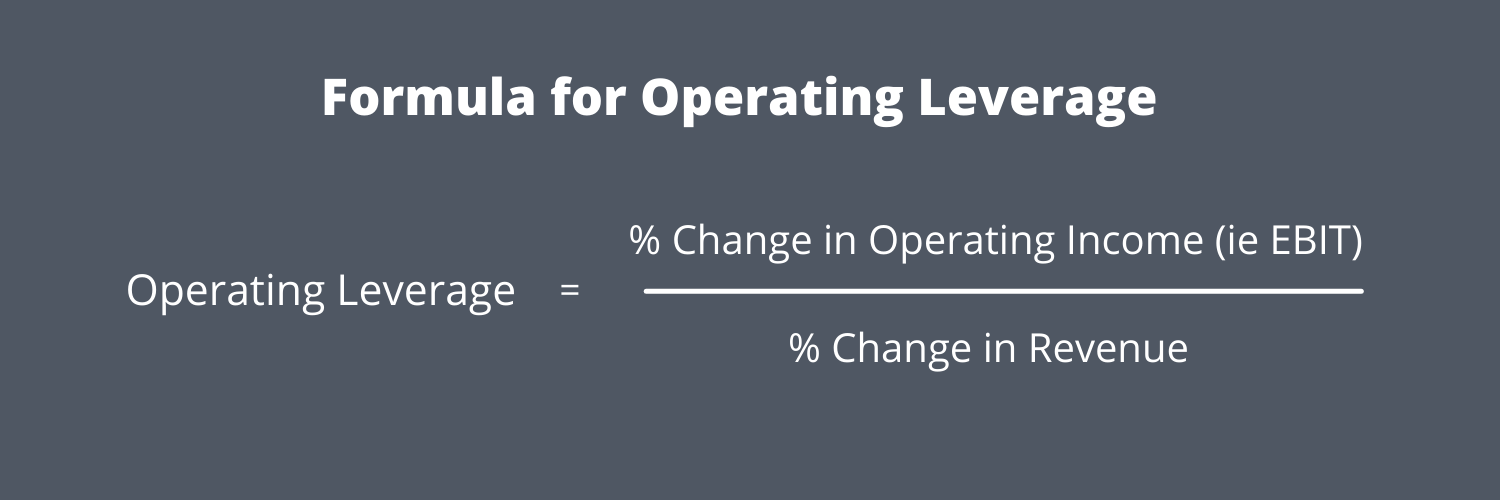
In practice, the formula most often used to calculate operating leverage tends to be dividing the change in operating income by the change in revenue. The benefit that results from this type of cost structure is that, if sales increase, the company’s profits will also increase correspondingly. Fixed costs do not vary with the volume of sales, whereas variable costs vary directly with sales volume. Most of Microsoft’s costs are fixed, such as expenses for upfront development and marketing. With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit, but Microsoft has high operating leverage.
Telecom Company Example
There are many alternative ways of calculating the degree of operating leverage. For illustration, let’s say a software company has invested $10 million into development and marketing for its latest application program, which sells for $45 per copy. Yes, but ensure you’re comparing companies within the same industry or sector, as operating leverage can vary significantly between different types of businesses. The only difference now is that the number of units sold is 5mm higher in the upside case and 5mm lower in the downside case. Companies with high DOLs have the potential to earn more profits on each incremental sale as the business scales.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
The DOL of a firm gives an instant look into the cost structure of the firm. The degree of operating leverage directly impacts the firm’s profitability. We already discussed that the higher operating leverage implies higher fixed costs.
Can I Use DOL to Compare Different Companies?
Higher DOL means higher operating profits (positive DOL), and negative DOL means operating loss. In fact, the relationship between sales revenue and EBIT is referred to as operating leverage because when the sales level increases or decreases, EBIT also changes. It is important to compare operating leverage between companies in the same industry, as some industries have higher fixed costs than others. For example, Company A sells 500,000 products for a unit price of $6 each. Financial and operating leverage are two of the most critical leverages for a business. Besides, they are related because earnings from operations can be boosted by financing; meanwhile, debt will eventually be paid back by those increased earnings.
Can DOL be used to compare companies?
The financial leverage ratio divides the % change in sales by the % change in earnings per share (EPS). You then take DOL and multiply it by DFL (degree of financial leverage). As a business owner or manager, it is important to be aware of the company’s cost structure and how changes in revenue will impact earnings. Additionally, investors should also keep an eye on this ratio when considering an investment in a company. The degree of operating leverage can never be harmful since it is a two-positive numbers ratio, i.e., sales and operating income. Moreover, the negative operating leverage implies that the operating income decreases as the revenue increases, which is inconsistent with the traditional definition of operating leverage.
The degree of operating leverage shows the change in operating income to the change in the revenues or sales of a company. For example, mining businesses have the up-front expense of highly specialized equipment. Airlines have the expense of purchasing and software for accountants and bookkeepers maintaining their fleet of airplanes. Once they have covered their fixed costs, they have the ability to increase their operating income considerably with higher sales output. On the other hand, low sales will not allow them to cover their fixed costs.
The degree of operating leverage calculator is a tool that calculates a multiple that rates how much income can change as a consequence of a change in sales. In this article, we will learn more about what operating leverage is, its formula, and how to calculate the degree of operating leverage. Furthermore, from an investor’s point of view, we will discuss operating leverage vs. financial leverage and use a real example to analyze what the degree of operating leverage tells us. The degree of operating leverage (DOL) assists a company in quantifying its operational risk, i.e., the risk arising from its mix of fixed and variable costs. Calculate the new degree of operating leverage when there are changes of proportion of fixed and variable costs. The degree of operating leverage (DOL) analyzes the change of the company’s operating income due to changes in sales.
Because retailers sell a large volume of items and pay upfront for each unit sold, COGS increases as sales increase. One concept positively linked to operating leverage is capacity utilization, which is how much the company uses its resources to generate revenues. Increasing utilization infers increased production and sales; thus, variable costs should rise. If fixed costs remain the same, a firm will have high operating leverage while operating at a higher capacity.
