
If you have the percentual change (period to period) of sales, put it here. Otherwise, add the specific period data in the section “Period to period specific data” above. For the particular case of the financial one, our handy return of invested capital calculator can measure its influence on the business outsourcing inventory management returns. The most authentic calculation method after the percentage change method is the ‘Sales minus Variable costs’ method. Operating leverage is the most authentic way of analyzing the cost structure of any business. DOL is based on historical data and may not accurately predict future performance.
The Operating Leverage Formula Is:
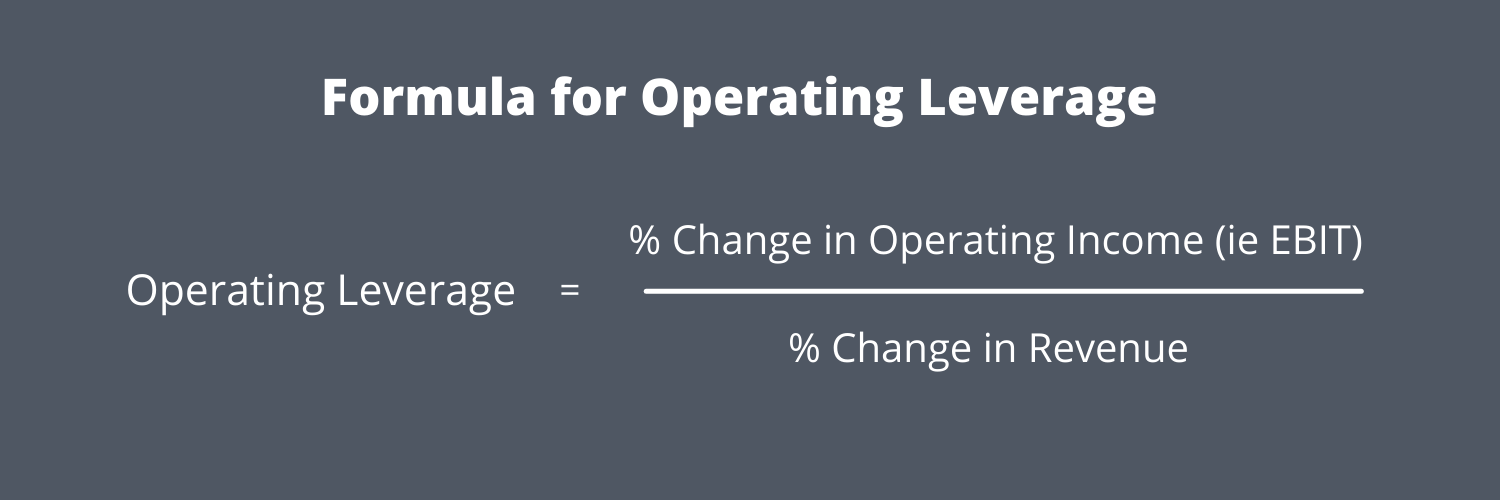
The DOL is calculated by dividing the contribution margin by the operating margin. For example, the DOL in Year 2 comes out 2.3x after dividing 22.5% (the change in operating income from Year 1 to Year 2) by 10.0% (the change in revenue from Year 1 to Year 2). However, since the fixed costs are $100mm regardless of the number of units sold, the difference in operating margin among the cases is substantial.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
For instance, if a company has a higher fixed-costs-to-variable-costs ratio, the fixed costs exceed variable costs. As can be seen from the example, the company’s degree of operating leverage is 1.0x for both years. This ratio helps managers and investors alike to identify how a company’s cost structure will affect earnings.
- For example, a DOL of 2 means that if sales increase (decrease) by 50%, operating income is expected to increase (decrease) by twice, i.e., 100%.
- If fixed costs remain the same, a firm will have high operating leverage while operating at a higher capacity.
- So, if there is a downturn in the economy, earnings don’t just fall, they can plummet.
- The shared characteristic of low DOL industries is that spending is tied to demand, and there are more potential cost-cutting opportunities.
- It helps predict the impact of any change in sales on company earnings.
Degree of Total Leverage (DTL)
However, if sales fall by 10%, from $1,000 to $900, then operating income will also fall by 10%, from $100 to $90. As such, the DOL ratio can be a useful tool in forecasting a company’s financial performance. Degree of operating leverage closely relates to the concept of financial leverage, which is a key driver of shareholder value. Investors can come up with a rough estimate of DOL by dividing the change in a company’s operating profit by the change in its sales revenue. For instance, a 10% increase in sales for a company with low DOL might result in a less than 10% increase in EBIT, indicating a more stable, albeit less responsive, profit scenario.
Unfortunately, unless you are a company insider, it can be very difficult to acquire all of the information necessary to measure a company’s DOL. Consider, for instance, fixed and variable costs, which are critical inputs for understanding operating leverage. It would be surprising if companies didn’t have this kind of information on cost structure, but companies are not required to disclose such information in published accounts.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
A company with low operating leverage has a large proportion of variable costs—which means that it earns a smaller profit on each sale, but does not have to increase sales as much to cover its lower fixed costs. The operating leverage is a financial ratio that measures the degree of operating risk. It is the relationship between fixed and variable costs and is calculated by dividing the change in operating income over the change in sales.
The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
The enterprise invests in fixed assets aiming for the volume to produce revenues that cover all fixed and variable costs. The degree of operating leverage (DOL) measures how much change in income we can expect as a response to a change in sales. In other words, the numerical value of this ratio shows how susceptible the company’s earnings before interest and taxes are to its sales. Basically, when there is a shift to more fixed operating costs in relative to variable operating cost, there will be greater degree of operating leverage. If the ratio is less than one, the one percent change in sales will lead to less change in operating income.
