
Price to earnings is a good measure of how expensive a stock is but does not take into account the company’s future growth prospects. Financial leverage is a more relative measure of the company’s debt for acquiring the fixed assets to use. Higher financial leverage represents the high volatility of a company’s earnings per share by a change in EBIT.
Why Use a Degree of Operating Leverage Calculator?
So, once the company has sold enough copies to cover its fixed costs, every additional dollar of sales revenue drops into the bottom line. In other words, Microsoft possesses remarkably high operating leverage. If the composition of a company’s cost structure is mostly fixed costs (FC) relative to variable costs (VC), the business model of the company is implied to possess a higher degree of operating leverage (DOL). DOL measures how sensitive a company’s operating income is to changes in product demand, as measured by unit sales.
Formula and Calculation of Degree of Operating Leverage
- As you can see from the example above, when there are changes in the proportion of fixed and variable operating costs, the degree of operating leverage will change.
- This can be beneficial in periods of rising sales but risky when sales decline.
- These calculators are important because as critical as it is to know how the business is doing, the price you are paying for a part of the company is also important.
- In other words, every additional product sold costs the business money.
It means 1% change in sales will lead to 0.8% (1% x 0.8) change in operating income. The revenues of company XYZ are $ 58.6 million, and that of company LMN are $ 32.7 million. The variable costs of company XYZ and company LMN are $25.7 million and $14.56 million. Similarly, the fixed costs of company XYZ and company LMN are $10.9 million and $6.54 million.
Examples
It helps predict the impact of any change in sales on company earnings. Companies or firms with a large proportion of variable costs to fixed costs have higher degrees of operating leverage and vice versa. Operating leverage measures a company’s ability to increase its operating income by increasing its sales volume. As a cost accounting measure, it is used to analyze the proportion of a company’s fixed versus variable costs. Essentially, operating leverage boils down to an analysis of fixed costs and variable costs.
How Does High Operating Leverage Affect My Business?
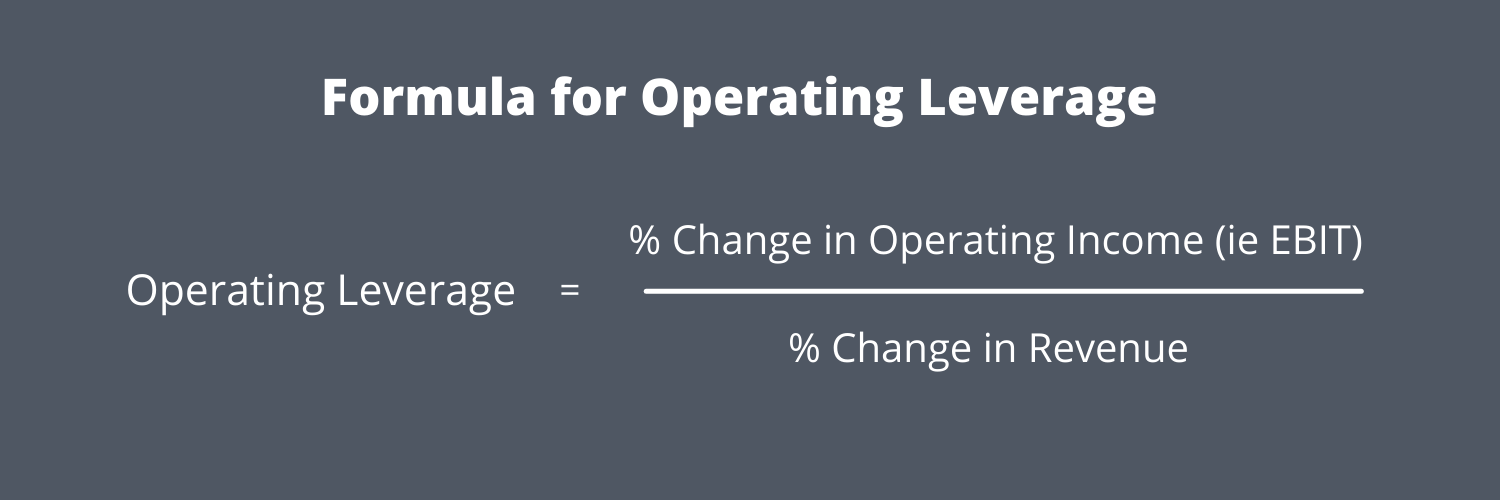
More sensitive operating leverage is considered riskier since it implies that current profit margins are less secure moving into the future. Companies with high fixed costs relative to variable costs will exhibit high operating leverage, meaning their earnings are more volatile with changes in sales. This can be beneficial in periods of rising sales but risky when sales decline. In the base case, the ratio between the fixed costs and the variable costs is 4.0x ($100mm ÷ $25mm), while the DOL is 1.8x – which we calculated by dividing the contribution margin by the operating margin. Similarly, a lower degree of operating leverage indicates that a business has a higher cost of variable ratio.
Ask Any Financial Question
If a company expects an increase in sales, a high degree of operating leverage will lead to a corresponding operating income increase. But if a company is expecting a sales decrease, tax software for accountants bookkeepers and tax agents a high degree of operating leverage will lead to an operating income decrease. It does this by measuring how sensitive a company is to operating income sales changes.
The high leverage involved in counting on sales to repay fixed costs can put companies and their shareholders at risk. High operating leverage during a downturn can be an Achilles heel, putting pressure on profit margins and making a contraction in earnings unavoidable. Indeed, companies such as Inktomi, with high operating leverage, typically have larger volatility in their operating earnings and share prices. Higher fixed costs lead to higher degrees of operating leverage; a higher degree of operating leverage creates added sensitivity to changes in revenue.
This includes the key definition, how to calculate the degree of operating leverage as well as example and analysis. Before, jumping into detail, let’s understand some key relevant definitions. Still, it gives many useful insights about a company’s operating leverage and ability to handle fluctuations and major economic events. The degree of financial leverage is a more mainstream ratio used by businesses for accessing the sensitivity of earnings per share by the change in the EBIT. For a low degree of operating leverage, the short-term revenue fluctuation doesn’t hurt the company’s profitability to a larger extent. Understanding the degree of operating leverage and its impact on the company’s financial health.
